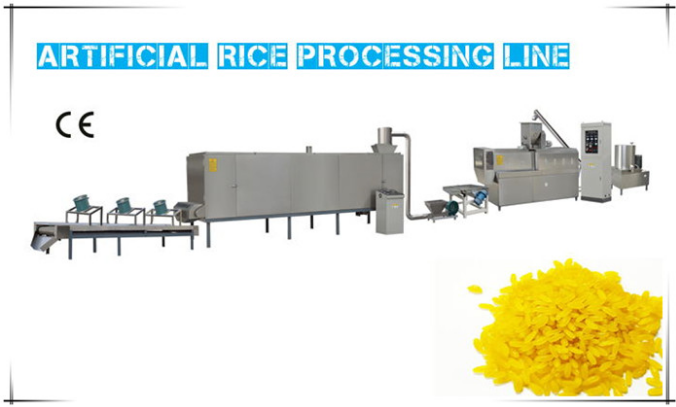
The fortified rice production line has gained popularity worldwide due to its potential to address malnutrition and improve public health. Fortified rice is rice that has been enhanced with essential nutrients to combat nutrient deficiencies, particularly in populations heavily reliant on rice as a staple food. In this news, I will discuss the reasons why the fortified rice production line is so popular.
1. Nutritional Enhancement:
Fortified rice production lines allow for the addition of essential nutrients to rice, such as vitamins and minerals. Common fortificants include vitamin A, iron, zinc, folic acid, and other B vitamins. These nutrients are crucial for overall health and well-being, and fortifying rice helps combat micronutrient deficiencies prevalent in many populations, particularly in developing countries. By enriching rice, the production line contributes to improving the nutritional status of individuals who rely on rice as their primary food source.

2. Staple Food Utilization:
Rice is a staple food for a significant portion of the global population, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. By fortifying rice, a commonly consumed food, the fortified rice production line provides an effective means to deliver essential nutrients to a large number of people. It takes advantage of the existing consumption patterns and ensures the availability of fortified food without requiring significant changes in dietary habits.
3. Cost-Effectiveness:
Fortifying rice can be a cost-effective strategy compared to other approaches to address nutrient deficiencies. Rice fortification leverages the existing rice production and distribution infrastructure, requiring minimal modifications to the supply chain. This makes it an efficient and affordable method to reach large populations, especially in resource-limited settings. Additionally, the cost of fortification can be relatively low, especially when compared to alternative interventions like supplementation or dietary diversification.
4. Technical Feasibility:
The fortified rice processing line has demonstrated technical feasibility, as it builds upon existing food processing technologies. The process typically involves coating rice kernels with a nutrient premix using specialized equipment. This equipment is readily available and can be integrated into rice processing facilities with relative ease. The technology is scalable and can be adapted to various production capacities, making it accessible to both small-scale and large-scale rice millers.
5. Food Safety and Stability:
Fortified rice production lines ensure that the added nutrients remain stable and bioavailable throughout the shelf life of the fortified rice. The chosen fortificants undergo rigorous testing to ensure they are safe for consumption and do not affect the sensory attributes or cooking properties of rice. The fortification process is carefully controlled to maintain the desired nutrient levels, ensuring the nutritional quality and safety of the fortified rice.
6. Public Health Impact:
Fortified rice production lines have the potential to make a significant impact on public health. By addressing nutrient deficiencies, particularly those related to vitamin A, iron, and zinc, fortified rice can help prevent various health conditions and improve overall well-being. For example, fortifying rice with vitamin A can help combat vitamin A deficiency, a leading cause of blindness and immune system impairments. Iron and zinc fortification can help reduce anemia and support proper growth and development in children.
7. Support from International Organizations:
The fortified rice production line has gained support from international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF), and Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN). These organizations recognize the potential of fortified rice to address malnutrition and have actively promoted its adoption as part of comprehensive nutrition strategies. Their advocacy and technical support have contributed to the popularity and acceptance of the fortified rice production line.
Conclusion
The fortified rice production line is popular due to its ability to enhance the nutritional value of rice, leverage existing consumption patterns, cost-effectiveness, technical feasibility, food safety, and its potential to make a significant impact on public health. By fortifying rice with essential nutrients, the production line offers a scalable and accessible solution to address nutrient deficiencies, particularly in regions heavily reliant on rice as a staple food.