Extrusion is a versatile and widely used process in the food industry, revolutionizing the way we produce various food products. It involves the application of pressure, heat, and mechanical force to transform raw ingredients into a wide range of shapes, sizes, and textures. This transformative technology has had a profound impact on food processing, leading to the creation of snacks, cereals, pasta, pet food, and even meat substitutes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how extrusion is used in food processing, examining its work principles, applications, and advantages.
Understanding the Basics of Food Extrusion
The Work Principle:
At its core, food extrusion is a mechanical and thermal process that involves forcing a food mixture or dough through a specially designed extruder machine. The machine typically consists of a barrel with a rotating screw or auger inside. As the food mixture travels through the barrel, it is subjected to heat and pressure, causing it to soften, expand, and take on the desired shape. The final product is then cut or shaped into the desired form as it exits the extruder.
Key Components of an Extruder:
1. Hopper: The hopper is the entry point where the raw ingredients are introduced into the extruder.
2. Screw or Auger: The screw is the heart of the extruder, responsible for conveying and compressing the food mixture as it moves through the barrel.
3. Barrel: The barrel surrounds the screw and is equipped with heating elements to provide the necessary thermal energy.
4. Die or Nozzle: The die or nozzle is located at the end of the barrel and determines the final shape and size of the extruded food product.
5. Cutting Mechanism: In some extrusion processes, a cutting mechanism is employed to trim or shape the product as it exits the extruder.

<p
Applications of Extrusion in Food Processing
1. Snack Foods:
Extrusion is perhaps most famous for its role in creating a wide range of snack foods. Popular snacks like extruded potato chips, cheese puffs, and breakfast cereals owe their unique shapes and textures to the extrusion process. The work principle in snack production involves precisely controlling temperature, pressure, and ingredients to achieve the desired taste and texture.
2. Pasta Production:
Extrusion has revolutionized pasta manufacturing, making it more efficient and versatile. Pasta dough is extruded through specialized dies to create various shapes such as spaghetti, macaroni, and fusilli. The work principle in pasta extrusion relies on the precise formulation of semolina or wheat flour, water, and sometimes eggs.
3. Breakfast Cereals:
Extrusion is a key technology in the production of breakfast cereals. Cereal grains are mixed with other ingredients and extruded to create familiar shapes like flakes, loops, or puffs. The work principle in cereal extrusion involves cooking the cereal mixture under controlled conditions to achieve the desired texture and flavor.
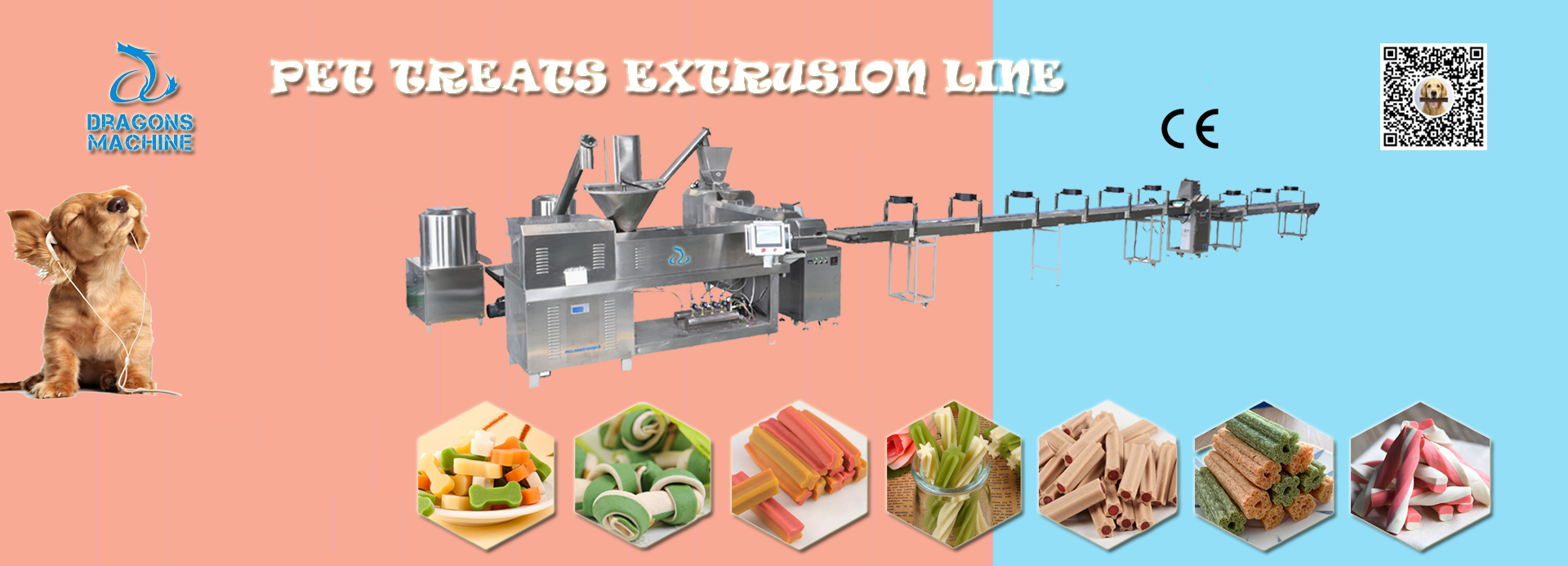
4. Pet Food:
The pet food industry also relies on extrusion to create nutritious and convenient pet food products. Extruded pet food can be tailored to specific dietary requirements and shapes. The work principle involves using a combination of meat, grains, and additives to produce balanced and palatable pet food.
5. Meat Alternatives:
Extrusion is increasingly used in the production of meat alternatives like plant-based burgers and sausages. Plant-based protein sources, such as soy or pea protein, are mixed with other ingredients and extruded to mimic the texture and taste of meat. The work principle here involves careful formulation and extrusion conditions to achieve the desired meat-like texture.
6. Baby Food:
Extrusion is applied to create convenient and nutritious baby food products. Ingredients like fruits, vegetables, and grains are processed into extruded purees and cereals, offering infants easy-to-digest options. The work principle emphasizes maintaining the nutritional integrity of the ingredients while ensuring product safety.
7. Confectionery:
Extrusion is used to create various confectionery products, including gummies, licorice, and even chocolate-filled bars. The work principle in confectionery extrusion involves precisely controlling the ingredients and temperatures to achieve the desired texture and flavor.
Advantages of Extrusion in Food Processing
The utilization of extrusion in food processing offers several significant advantages:
1. Versatility:
Extrusion can create a wide range of food products with diverse textures, shapes, and sizes, making it a versatile technology for the food industry.
2. Efficiency:
Extrusion is a continuous process that allows for high production rates and reduced labor costs compared to traditional methods.
3. Control Over Product Attributes:
The work principle in extrusion enables precise control over parameters such as temperature, pressure, and ingredient composition, resulting in consistent product quality.
4. Enhanced Nutritional Value:
Extrusion can improve the nutritional value of food products by increasing the bioavailability of certain nutrients and reducing antinutritional factors.
5. Extended Shelf Life:
Extruded products often have a longer shelf life due to reduced moisture content and improved resistance to spoilage.
6. Customization:
Extrusion allows for product customization to meet specific consumer preferences and dietary requirements.
Conclusion
Extrusion is a transformative technology that has reshaped the food industry by offering efficiency, versatility, and control over product attributes. The work principle behind food extrusion involves the precise application of pressure, heat, and mechanical force to create a wide range of food products, from snacks and pasta to pet food and meat alternatives. As the food industry continues to evolve, extrusion remains a fundamental tool for innovating and meeting the diverse needs and preferences of consumers.